Cybersecurity Website
Malware
Malware, short for malicious software, refers to any software intentionally designed to cause damage to a computer, server, client, or computer network. It can take the form of viruses, worms, trojans, ransomware, spyware, adware, and more.
Types of Malware
- Viruses: Programs that attach themselves to legitimate files and spread when executed.
- Worms: Standalone malware that replicates itself to spread to other computers.
- Trojans: Malicious software disguised as legitimate software.
- Ransomware: Blocks access to data or systems until a ransom is paid.
How to Protect Against Malware
- Install and update antivirus software regularly.
- Avoid downloading files or clicking on links from unknown sources.
- Keep your operating system and software up to date.
- Use firewalls to block unauthorized access.
Notable Malware Examples

ILOVEYOU Virus
1999A computer worm that spread through email in 2000, causing billions in damages. It was disguised as a love letter, but it was actually a destructive virus hidden with a VBS script.
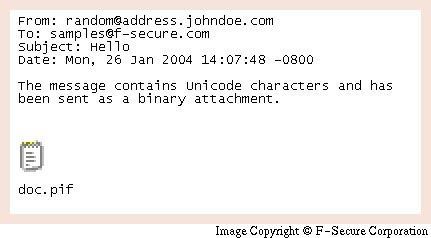
MyDoom
2004One of the fastest-spreading email worms, causing an estimated $38 billion in damages. It spread through email attachments and was designed to create a backdoor in the infected system.