Cybersecurity Website
Ransomware
Ransomware is a type of malicious software that encrypts a victim's files or blocks access to a computer system until a ransom is paid. It has become one of the most significant cyber threats facing individuals and organizations today.
How Ransomware Works
- Infection: Usually spread through phishing emails, exploit kits, or compromised websites.
- Encryption: Once installed, ransomware encrypts files using strong encryption algorithms.
- Ransom Demand: The attacker demands payment (often in cryptocurrency) for the decryption key.
- Timer: Many ransomware variants include a countdown timer, threatening to destroy the key if payment isn't made.
Protecting Against Ransomware
- Maintain regular, offline backups of important data.
- Keep all software and operating systems updated with the latest security patches.
- Use reputable security software and keep it updated.
- Be cautious when opening email attachments or clicking on links.
- Implement network segmentation to limit the spread of ransomware within an organization.
What to Do If You're Infected
- Disconnect the infected device from all networks immediately.
- Report the attack to law enforcement (FBI's Internet Crime Complaint Center).
- Consult with cybersecurity professionals before considering paying the ransom.
- Restore systems from clean backups if available.
Ransomware Examples
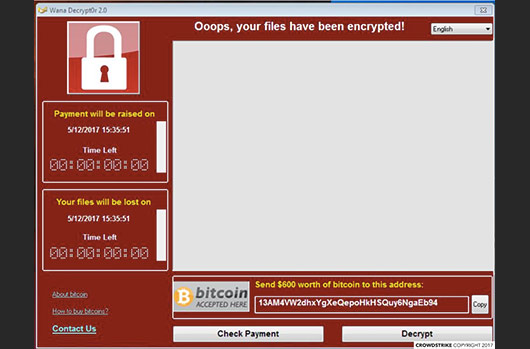
WannaCry
2017A global ransomware attack that affected hundreds of thousands of computers in over 150 countries in May 2017. It exploited a vulnerability in Windows systems and demanded payment in Bitcoin.
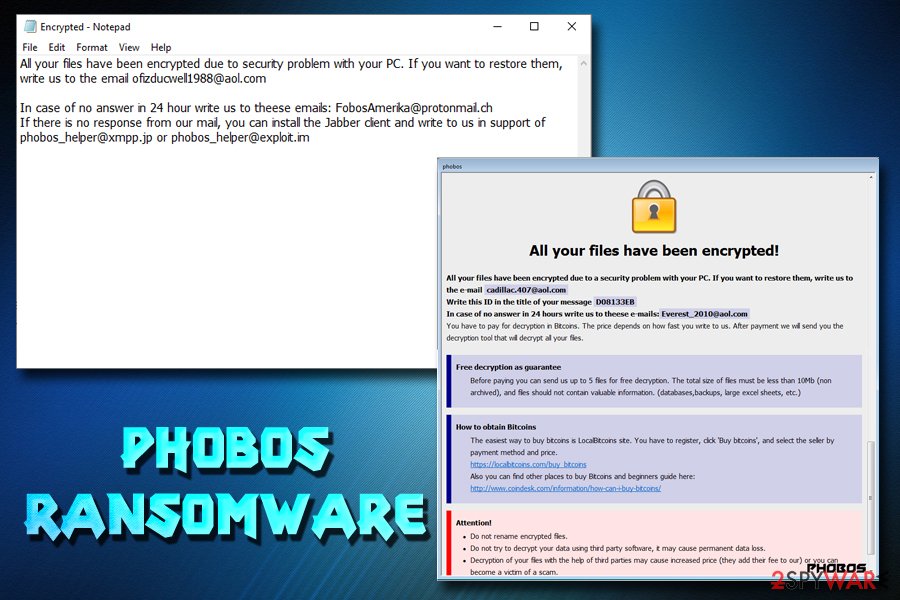
Phobos
2020A ransomware variant that targets various industries and has been linked to multiple attacks worldwide.